Estimating effect of multiple treatments
[1]:
from dowhy import CausalModel
import dowhy.datasets
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
[2]:
data = dowhy.datasets.linear_dataset(10, num_common_causes=4, num_samples=10000,
num_instruments=0, num_effect_modifiers=2,
num_treatments=2,
treatment_is_binary=False,
num_discrete_common_causes=2,
num_discrete_effect_modifiers=0,
one_hot_encode=False)
df=data['df']
df.head()
[2]:
| X0 | X1 | W0 | W1 | W2 | W3 | v0 | v1 | y | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -0.160726 | 0.197717 | 0.168884 | 0.281044 | 0 | 2 | 7.305433 | 1.566046 | 96.418483 |
| 1 | 0.622458 | 1.749118 | 1.266611 | -0.697390 | 3 | 3 | 22.841898 | 17.612662 | 4068.381933 |
| 2 | -0.507455 | 0.239130 | -0.343174 | 0.415110 | 0 | 2 | 3.728880 | 2.577602 | 59.251898 |
| 3 | -0.762805 | -0.040333 | -2.167921 | -0.418095 | 2 | 1 | -3.357920 | 7.994089 | 131.406754 |
| 4 | -1.552625 | 0.831265 | 1.186141 | -0.322733 | 2 | 3 | 19.853591 | 15.394102 | -437.483542 |
[3]:
model = CausalModel(data=data["df"],
treatment=data["treatment_name"], outcome=data["outcome_name"],
graph=data["gml_graph"])
[4]:
model.view_model()
from IPython.display import Image, display
display(Image(filename="causal_model.png"))
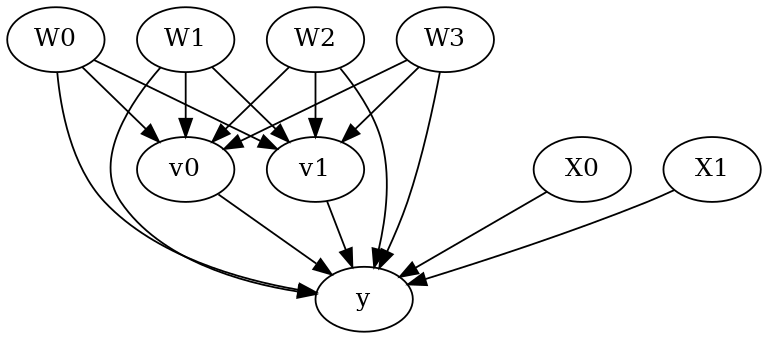
[5]:
identified_estimand= model.identify_effect(proceed_when_unidentifiable=True)
print(identified_estimand)
Estimand type: EstimandType.NONPARAMETRIC_ATE
### Estimand : 1
Estimand name: backdoor
Estimand expression:
d
─────────(E[y|W0,W3,W2,W1])
d[v₀ v₁]
Estimand assumption 1, Unconfoundedness: If U→{v0,v1} and U→y then P(y|v0,v1,W0,W3,W2,W1,U) = P(y|v0,v1,W0,W3,W2,W1)
### Estimand : 2
Estimand name: iv
No such variable(s) found!
### Estimand : 3
Estimand name: frontdoor
No such variable(s) found!
Linear model
Let us first see an example for a linear model. The control_value and treatment_value can be provided as a tuple/list when the treatment is multi-dimensional.
The interpretation is change in y when v0 and v1 are changed from (0,0) to (1,1).
[6]:
linear_estimate = model.estimate_effect(identified_estimand,
method_name="backdoor.linear_regression",
control_value=(0,0),
treatment_value=(1,1),
method_params={'need_conditional_estimates': False})
print(linear_estimate)
*** Causal Estimate ***
## Identified estimand
Estimand type: EstimandType.NONPARAMETRIC_ATE
### Estimand : 1
Estimand name: backdoor
Estimand expression:
d
─────────(E[y|W0,W3,W2,W1])
d[v₀ v₁]
Estimand assumption 1, Unconfoundedness: If U→{v0,v1} and U→y then P(y|v0,v1,W0,W3,W2,W1,U) = P(y|v0,v1,W0,W3,W2,W1)
## Realized estimand
b: y~v0+v1+W0+W3+W2+W1+v0*X1+v0*X0+v1*X1+v1*X0
Target units: ate
## Estimate
Mean value: 19.38227351230603
You can estimate conditional effects, based on effect modifiers.
[7]:
linear_estimate = model.estimate_effect(identified_estimand,
method_name="backdoor.linear_regression",
control_value=(0,0),
treatment_value=(1,1))
print(linear_estimate)
*** Causal Estimate ***
## Identified estimand
Estimand type: EstimandType.NONPARAMETRIC_ATE
### Estimand : 1
Estimand name: backdoor
Estimand expression:
d
─────────(E[y|W0,W3,W2,W1])
d[v₀ v₁]
Estimand assumption 1, Unconfoundedness: If U→{v0,v1} and U→y then P(y|v0,v1,W0,W3,W2,W1,U) = P(y|v0,v1,W0,W3,W2,W1)
## Realized estimand
b: y~v0+v1+W0+W3+W2+W1+v0*X1+v0*X0+v1*X1+v1*X0
Target units: ate
## Estimate
Mean value: 19.38227351230603
More methods
You can also use methods from EconML or CausalML libraries that support multiple treatments. You can look at examples from the conditional effect notebook: https://py-why.github.io/dowhy/example_notebooks/dowhy-conditional-treatment-effects.html
Propensity-based methods do not support multiple treatments currently.